연결리스트
연결리스트란?
여러개의 노드들이 순차적으로 연결된 형태를 갖는 자료그조이다.
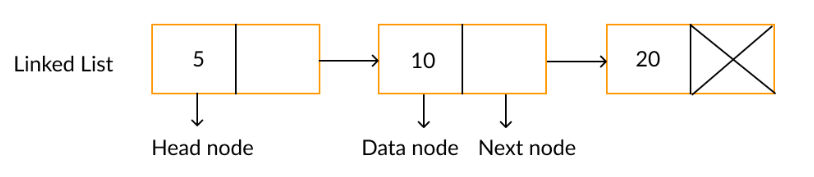
제일 앞에 있는 노드를 head, 제일 뒤에 있는 노드를 tail이라고 하며, 각 노드들은 데이터와 다음 노드를 가르키는 포인터로 이루어져있다.
tree 구조에서 각 노드들은 연결리스트로 구현되어 있다.
head,tail노드와 더미 노드
head와 tail에도 데이터 필드가 있지만, 쓰지 않는 편이 구현에 있어 용이하다.
만약 데이터 필드를 쓰게 되면 추가, 삭제시 3가지를 고려해야하기 때문이다.
- 추가, 삭제할 노드가 맨 앞 노드인가
- 추가, 삭제할 노드가 맨 뒤 노드인가
- 추가, 삭제할 노드가 중간 노드인가
만약 head, tail의 데이터 필드를 사용하지 않는다면 3번 조건만 고려하면 되기 때문에 용이하다.
이러한 데이터가 없는 노드를 더미노드라고 한다.
시간 복잡도
- 탐색 : O(n)
- 삽입/삭제 :
- 노드 삽입과 노드 삭제 : O(1)
- 삽입 삭제를 위한 탐색 : O(n)
=> 전체 삽입/삭제 : O(n)
배열과 연결리스트 비교
배열과 비교해서 탐색을 처음부터 진행해야해서 많은 시간이 소요된다.
하지만 삽입,삭제가 빨라서 삽입, 삭제가 빈번한 경우에 좋다.
구현
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if not self.head:
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
def prepend(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def delete(self, data):
if not self.head:
return
if self.head.data == data:
self.head = self.head.next
return
current = self.head
while current.next:
if current.next.data == data:
current.next = current.next.next
return
current = current.next
def display(self):
elements = []
current = self.head
while current:
elements.append(current.data)
current = current.next
print(" -> ".join(map(str, elements))
# 연결 리스트를 생성하고 사용하는 예제
if __name__ == "__main__":
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.append(1)
linked_list.append(2)
linked_list.append(3)
linked_list.prepend(0)
linked_list.display() # 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3
linked_list.delete(2)
linked_list.display() # 0 -> 1 -> 3